Tibbspaving

News & Events
Tibbspaving
Accessible Parking
ADA National Network / 07-16-2021 Accessible Parking
Accessible Parking
These revised rules affect state and local governments (Title II of the ADA), as well as public accommodations and commercial facilities (Title III). The regulations require compliance with 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design, outlining minimum accessibility requirements for buildings and facilities.
Existing Facilities
New construction projects must meet minimum standards with very few exceptions; alterations are also subject to strict requirements, although they may be more affected by existing structural conditions. Existing buildings and facilities which are not undergoing planned alterations are viewed a little differently
Title II: Program Access
State and local government agencies that offer programs, services, or activities in existing facilities need to make sure that people with disabilities can gain access and participate in these activities. Adding accessible parking is one step government agencies can take to ensure people with disabilities can participate.
Title III: Barrier Removal
Public accommodations (private businesses that are open to the general public, like retail stores, restaurants, banks, parking garages, and many others) must remove barriers when it is “readily achievable” to do so; readily achievable means “easily accomplishable and able to be carried out without much difficulty or expense.” Designating accessible parking is often readily achievable and is considered a top priority because it enables many people with disabilities to “get in the door.
Safe Harbor
The 2010 Standards include a “safe harbor” for features that already comply with the 1991 Standards, but may not meet the new 2010 Standards.
For example: A retail store’s parking lot has a total of 250 parking spaces. In compliance with 1991 Standards, the lot includes seven accessible spaces, one of which is van-accessible. The 2010 Standards require two van-accessible spaces, but the store does not have to modify its parking lot to provide the additional space until the lot undergoes a planned alteration (re-striping, re-surfacing, etc.)Any alterations made after March 15, 2012 must comply with the 2010 Standards, to the maximum extent feasible.
How many accessible parking spaces are needed?
The minimum number of accessible parking spaces required depends on the total number of parking spaces in the lot, as seen in the table below. Furthermore, one of every six accessible parking spaces, or fraction of six, must be “van-accessible.” For example: A parking lot with 400 total spaces needs eight accessible spaces, and two of those eight spaces must be van-accessible.
Medical Facilities
Certain types of medical facilities need more accessible parking.
- Hospital outpatient facilities need 10% of patient/visitor spaces to be accessible.
- Rehabilitation facilities that specialize in treating mobility-related conditions and outpatient physical therapy facilities need 20% of patient/visitor spaces to be accessible.
The number of van-accessible spaces is one of every six accessible parking spaces, or fraction of six.
For example: An outpatient physical therapy facility has a parking lot with 50 total spaces for employees only. The lot needs two accessible spaces, one of which must be van-accessible. A separate lot with 200 total spaces for patients and visitors needs 40 accessible spaces, seven of which must be van accessible.
Exceptions
Parking facilities that are used exclusively for buses, trucks, delivery vehicles, law enforcement vehicles, and vehicular impound are not required to include accessible spaces. However, if such lots are accessed by the public (e.g., impounded vehicle retrieval), an accessible passenger loading zone must be provided.
Location
Accessible spaces must connect to the shortest accessible route to the accessible building entrance or facility they serve.
- If a parking facility serves multiple buildings or accessible entrances, accessible parking spaces should be dispersed to enable people to park near as many accessible entrances as possible.
For example: A shopping center has fifteen stores, each with a separate entrance. There is one large parking lot with 1000 spaces. The twenty accessible parking spaces should be dispersed to provide some options for people to park close to the different stores.
- If separate parking facilities serve the same building or entrance, accessible spaces may be grouped together, as long as the number of spaces provided is determined according to each of the separate parking facilities.
For example: A sports stadium has an adjacent parking lot with 1000 spaces and a separate parking lot several blocks away with an additional 1500 spaces. The adjacent lot needs 20 accessible spaces (four of which need to be van-accessible), and the remote lot needs 25 accessible spaces (five of which need to be van-accessible). Since accessible spaces need to be as near as possible to the facilities they serve, the 45 accessible spaces (including nine vanaccessible) can be located in the lot adjacent to the stadium.
What do accessible parking spaces look like?
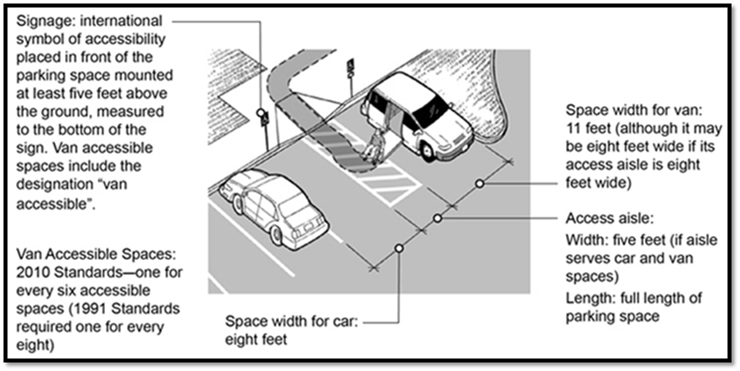
Design
Dimensions (all dimensions are minimums): Accessible parking spaces are eight (8) feet wide; van accessible spaces are eleven (11) feet wide. Access aisles for either type of space are five (5) feet wide. These adjacent aisles, which can be shared between two spaces, provide room for individuals to deploy vehicle-mounted wheelchair lifts and/or unload and use mobility devices such as wheelchairs, walkers, etc. An alternate design allows a van-accessible space to be eight (8) feet wide if the adjacent access aisle is also eight (8) feet wide.
Access aisles must be marked (e.g., painted with hatch marks) to discourage parking in them. This is especially important where the alternate design is used and an access aisle at a van-accessible space is the same size as the space.
The surface of accessible spaces and access aisles must be smooth, stable, and virtually level in all directions to ensure safe use for people with disabilities, including those who must load, unload, and use wheeled mobility devices.
Additionally, van-accessible spaces, their associated access aisles, and the vehicular routes serving them must provide vertical clearance of at least 98 inches to allow for the height of typical wheelchair lift-equipped vehicles.
Signs
Accessible parking spaces must be identified by signs that include the International Symbol of Accessibility. Signs at van-accessible spaces must include the additional phrase “van-accessible.” Signs should be mounted so that the lower edge of the sign is at least five (5) feet above the ground. This helps ensure visibility both for motorists and local enforcement officials.
Exceptions
- Small parking lots of four or fewer spaces must have accessible spaces, but those spaces do not need a sign and anyone, with or without a disability, can park in the accessible space. This is intended so very small entities do not have to reserve 25% to 100% of their available parking for individuals with disabilities.
- Residential facilities where parking spaces are assigned to specific dwelling units are also not required to post signs at accessible spaces. Note: These two exceptions only relate to signs; accessible parking spaces are still required.
Maintenance
Accessible parking spaces, aisles, and routes must be maintained in good repair and kept clear of snow, ice, or fallen leaf build-up.
Other Laws, Other Requirements
The ADA establishes these requirements to ensure that when parking facilities are provided by entities covered by Title II or Title III, accessible spaces with certain features are available. Many state and local governments have their own requirements, which may be more specific or more stringent.
Each state also establishes criteria and procedures to issue accessible parking permits (often in the form of distinctive license plates or placards) to individuals with disabilities. Enforcement activities related to these issues (fraudulent use of permits, illegal parking in accessible spaces, etc.) are typically carried out by state and local authorities, such as city police departments.
Other requirements may be relevant in different situations or under different laws. For example, the Fair Housing Act requires covered housing providers to make “reasonable accommodations” for residents with disabilities, which could mean reserving a parking space for a specific individual.
Article Source: www.adata.org

Tibbspaving
FREE Estimate
To receive a free estimate, please give us a call or complete this form.
Thank you!






